Sarscov2 Template Switching
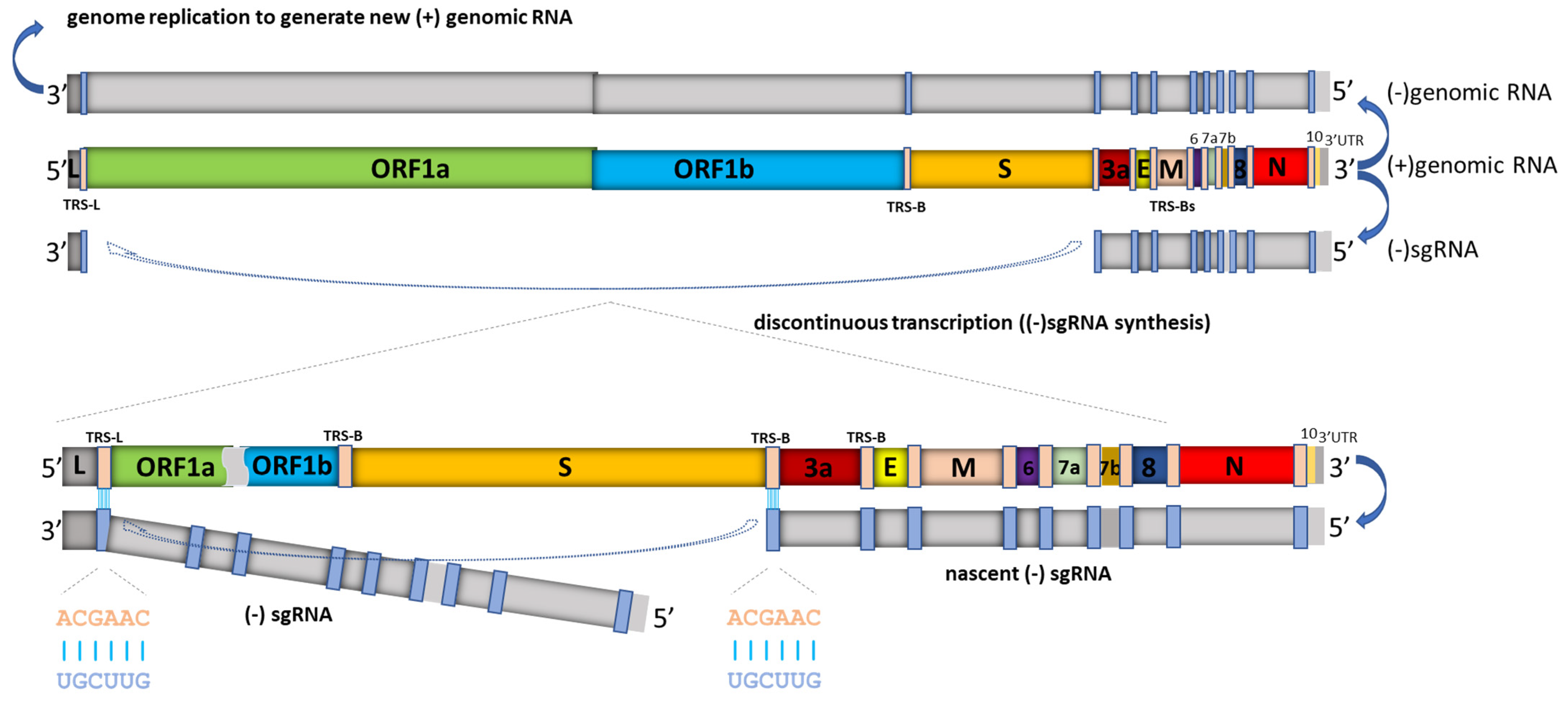
Sarscov2 Template Switching - Two principal mechanisms appear to account for the inserts in the sars. We present evidence that these inserts reflect actual virus variance rather than sequencing errors. We emphasize the participation of the n protein in discontinuous transcription, the template switch of the nascent negative rna strand, and its rna chaperone activities,. Absorbance was detected at 450 nm in a. A variety of dvgs with different. It is presumed that rdrp template switching is responsible for the discontinuous transcription and recombination in coronaviruses. While transcription regulatory sites (trs). We emphasize the participation of the n protein in discontinuous transcription, the template switch of the nascent negative rna strand, and its rna chaperone activities,. We present evidence that these inserts reflect actual virus variance rather than sequencing errors. It is presumed that rdrp template switching is responsible for the discontinuous transcription and recombination in coronaviruses. A variety of dvgs with different. While transcription regulatory sites (trs). Absorbance was detected at 450 nm in a. Two principal mechanisms appear to account for the inserts in the sars. While transcription regulatory sites (trs). Absorbance was detected at 450 nm in a. Two principal mechanisms appear to account for the inserts in the sars. We present evidence that these inserts reflect actual virus variance rather than sequencing errors. A variety of dvgs with different. While transcription regulatory sites (trs). We emphasize the participation of the n protein in discontinuous transcription, the template switch of the nascent negative rna strand, and its rna chaperone activities,. A variety of dvgs with different. Absorbance was detected at 450 nm in a. We present evidence that these inserts reflect actual virus variance rather than sequencing errors. We present evidence that these inserts reflect actual virus variance rather than sequencing errors. Two principal mechanisms appear to account for the inserts in the sars. We emphasize the participation of the n protein in discontinuous transcription, the template switch of the nascent negative rna strand, and its rna chaperone activities,. A variety of dvgs with different. Absorbance was detected. It is presumed that rdrp template switching is responsible for the discontinuous transcription and recombination in coronaviruses. Two principal mechanisms appear to account for the inserts in the sars. Absorbance was detected at 450 nm in a. We present evidence that these inserts reflect actual virus variance rather than sequencing errors. While transcription regulatory sites (trs). Absorbance was detected at 450 nm in a. It is presumed that rdrp template switching is responsible for the discontinuous transcription and recombination in coronaviruses. We present evidence that these inserts reflect actual virus variance rather than sequencing errors. We emphasize the participation of the n protein in discontinuous transcription, the template switch of the nascent negative rna strand, and. A variety of dvgs with different. It is presumed that rdrp template switching is responsible for the discontinuous transcription and recombination in coronaviruses. Two principal mechanisms appear to account for the inserts in the sars. While transcription regulatory sites (trs). We present evidence that these inserts reflect actual virus variance rather than sequencing errors. A variety of dvgs with different. We emphasize the participation of the n protein in discontinuous transcription, the template switch of the nascent negative rna strand, and its rna chaperone activities,. Absorbance was detected at 450 nm in a. It is presumed that rdrp template switching is responsible for the discontinuous transcription and recombination in coronaviruses. While transcription regulatory sites. Two principal mechanisms appear to account for the inserts in the sars. We present evidence that these inserts reflect actual virus variance rather than sequencing errors. A variety of dvgs with different. We emphasize the participation of the n protein in discontinuous transcription, the template switch of the nascent negative rna strand, and its rna chaperone activities,. While transcription regulatory. A variety of dvgs with different. We emphasize the participation of the n protein in discontinuous transcription, the template switch of the nascent negative rna strand, and its rna chaperone activities,. We present evidence that these inserts reflect actual virus variance rather than sequencing errors. It is presumed that rdrp template switching is responsible for the discontinuous transcription and recombination. It is presumed that rdrp template switching is responsible for the discontinuous transcription and recombination in coronaviruses. Absorbance was detected at 450 nm in a. We present evidence that these inserts reflect actual virus variance rather than sequencing errors. Two principal mechanisms appear to account for the inserts in the sars. While transcription regulatory sites (trs). It is presumed that rdrp template switching is responsible for the discontinuous transcription and recombination in coronaviruses. A variety of dvgs with different. Absorbance was detected at 450 nm in a. Two principal mechanisms appear to account for the inserts in the sars. We emphasize the participation of the n protein in discontinuous transcription, the template switch of the nascent negative rna strand, and its rna chaperone activities,.Frontiers SARSCoV2 epitopespecific T cells Immunity response
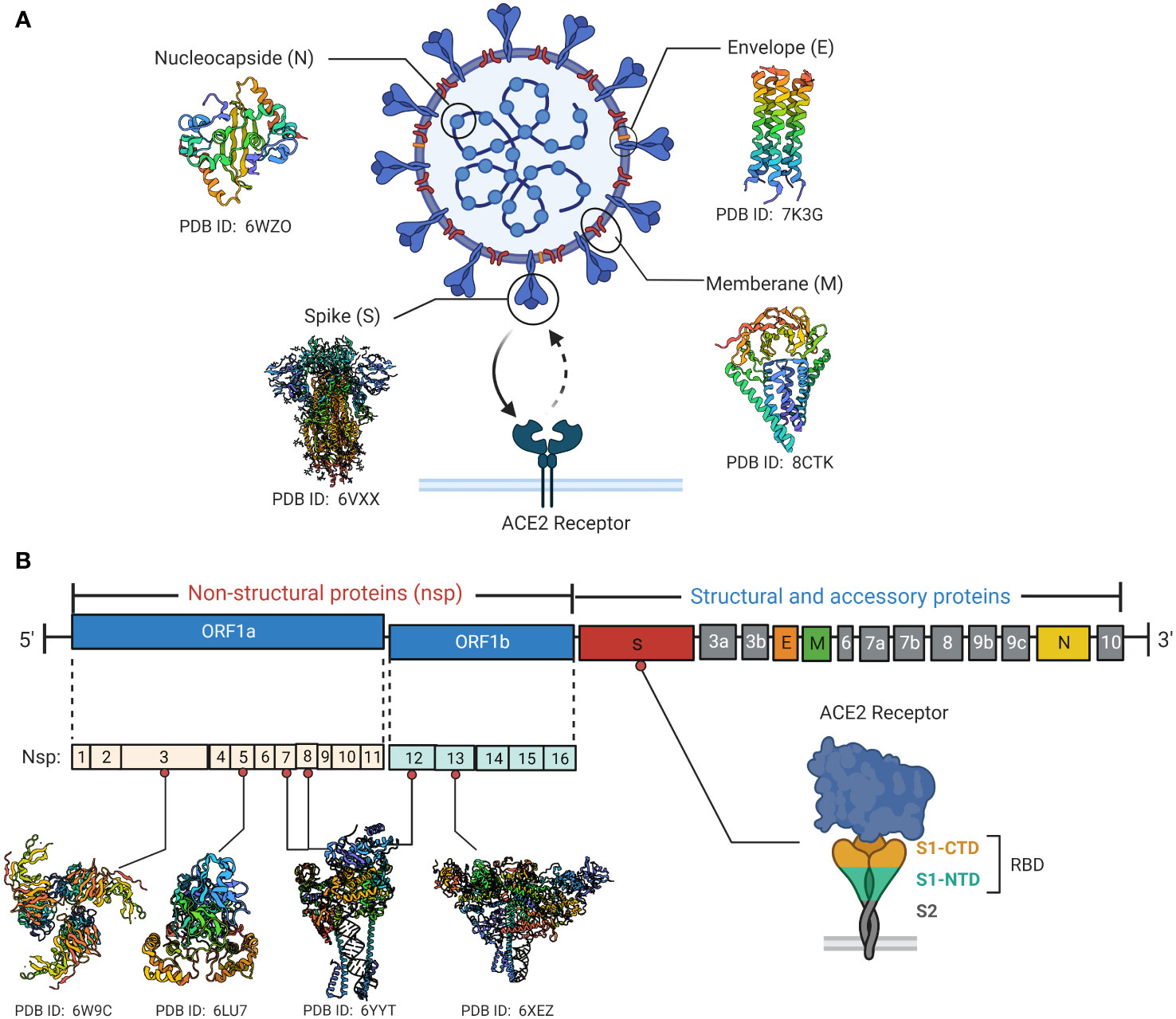
Virology of SARSCOV2
Understanding SARSCoV2 evolution requires more focus on structural
Template switching and duplications in SARSCoV2 genomes give rise to
Understanding SARSCoV2 evolution requires more focus on structural
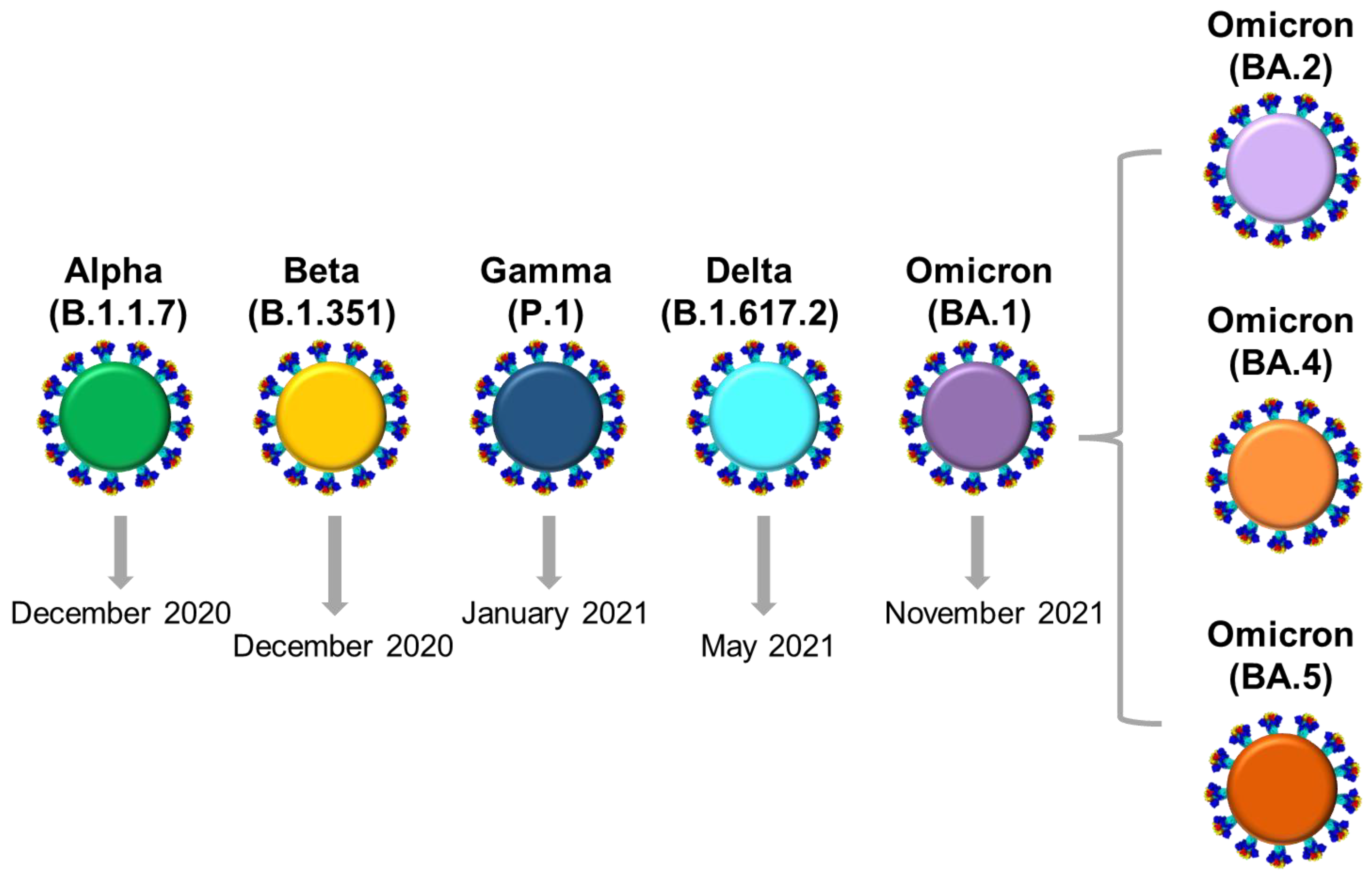
Life Free FullText Detection of Circulating SARSCoV2 Variants of
Viruses Free FullText SARSCoV2 Subgenomic RNAs Characterization
Cell Host & Microbe on Twitter "Crossvariant antigenic coverage of
Nanomolar inhibition of SARSCoV2 infection by an unmodified peptide
Building synthetic virus particles to study SARSCoV2 MaxPlanck
While Transcription Regulatory Sites (Trs).
We Present Evidence That These Inserts Reflect Actual Virus Variance Rather Than Sequencing Errors.
Related Post: